Nikola Schmidt
September 10,2024
Introduction
Water bath heater for fuel gas is a crucial component in various industrial processes, designed to efficiently and safely heat fuel gases before they enter the main processing system. This specialized heating system utilizes the principle of indirect heating, where the fuel gas flows through a coil or tube submerged in a bath of heated water.
The water bath serves as a heat transfer medium, ensuring a gradual and controlled elevation of the fuel gas temperature. This method prevents direct contact between the heating source and the gas, minimizing the risk of combustion or undesirable chemical reactions.
Water bath heaters are particularly employed in the oil and gas industry, where they play a vital role in preheating natural gases, liquefied petroleum gases (LPG), or other hydrocarbon streams, enhancing their flow characteristics and optimizing downstream processes.
The versatility and efficiency of water bath heaters make them integral for maintaining operational integrity and efficiency in diverse industrial applications.
How Water Bath Heaters Work
Water bath heaters are commonly used in the oil and gas industry to heat fuel gas before it enters a processing facility or a gas turbine. These heaters operate on the principle of indirect heating through the use of a bath of water or another heat transfer fluid. The basic design consists of a shell-and-tube heat exchanger submerged in a water-filled vessel.
Fuel gas flows through the tubes of the heat exchanger, while water surrounds the tubes in the outer shell. As the fuel gas passes through the tubes, heat is transferred from the water bath to the gas, raising its temperature to the desired level. The water bath absorbs the heat generated by a burner or an electric heater located beneath the vessel. This indirect heating method prevents direct contact between the flame or heating element and the fuel gas, minimizing the risk of combustion or degradation of the gas quality.
Water bath heaters offer several advantages, including uniform heating, ease of temperature control, and the ability to handle a wide range of flow rates. Additionally, they are well-suited for heating fuel gas with varying composition and impurities.
The water bath serves as an effective heat transfer medium, ensuring efficient and reliable heating of the fuel gas before it undergoes further processing or combustion in industrial applications.
Regular maintenance, such as monitoring water levels and inspecting for corrosion, is crucial to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of water bath heaters in fuel gas applications.
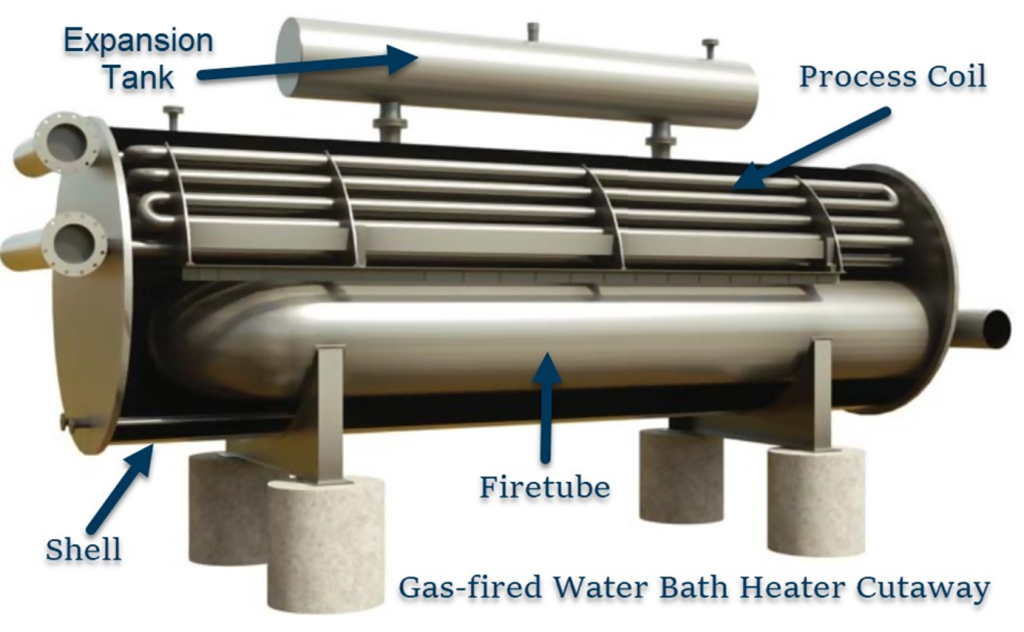
Heater Operation
The process to be heated flows through a serpentine configured coil that is mounted in the upper reaches of the heater shell. A controlled amount of heat is liberated into the fire-tube (combustion chamber) which is located in the lower reaches of the shell where heat is efficiently transferred from the fire-tube in both media. The heat contained in the bath media is then transferred by natural convection into the process stream which flows through the process coil.
The heater shell is an atmospheric vessel designed in according with specific requirements. The shell contains the process tube-bundle, fire-tube (Combustion chamber), and heat media.
The fire-tube is commonly of the U-tube configuration. The tube is removable & designed to efficiently transfer heat into the surrounding heat media and to minimize flue gas friction losses.
The process tube-bundle is a pressure containing part commonly designed in accordance with specific requirements.
The process to be heated flows through a serpentine configured coil that is mounted in the upper reaches of the heater shell. A controlled amount of heat is liberated into the fire-tube (combustion chamber) which is located in the lower reaches of the shell where heat is efficiently transferred from the fire-tube in both media. The heat contained in the bath media is then transferred by natural convection into the process stream which flows through the process coil.
The heater shell is an atmospheric vessel designed in according with specific requirements. The shell contains the process tube-bundle, fire-tube (Combustion chamber), and heat media.
The fire-tube is commonly of the U-tube configuration. The tube is removable & designed to efficiently transfer heat into the surrounding heat media and to minimize flue gas friction losses.
The process tube-bundle is a pressure containing part commonly designed in accordance with specific requirements.
MEDAS: Your Partner in Efficient Water Bath Heater Solutions
MEDAS understands the critical role water bath heaters play in your industrial processes. We offer fully customized solutions to ensure your heaters operate at peak efficiency. Explore our range of water bath heater services and discover how MEDAS can optimize your heating process.
For more details, visit our website: https://medasgmbh.com/en/the-business/energy-utility/indirect-water-bath-heaters